Earlier, large cables were used to connect drives. As the technologies progressed; RPMs and cache size increased, firmware and controllers matured. And then the old connection was replaced with SATA to allow for more speed and features t0 the user. As these newer SSDs hit the market, the SATA interface has become one process among the main processes. However, more advanced SSD controllers can allow for more lanes increasing the speeds. But the speed potentials of the SATA SSDs shackle down including the newest and the best SATA 6 Gb/s standard. Therefore a better alternative should come in handy.
In this article, we compare SATA SSDs with PCI Express.
SATA
Serial AT Attachment (SATA) is a connection interface type that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drivers and solid-state drivers and solid state drives. SATA has replaced the older used Parallel ATA (PATA), and it offers several advantages over the older interface. Some of the advantages that SATA comes with include reduced cost and cable size (7 conductors instead of 40 or 80), faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, more efficient transfer through an optional I/O queuing protocol and native hot swapping.
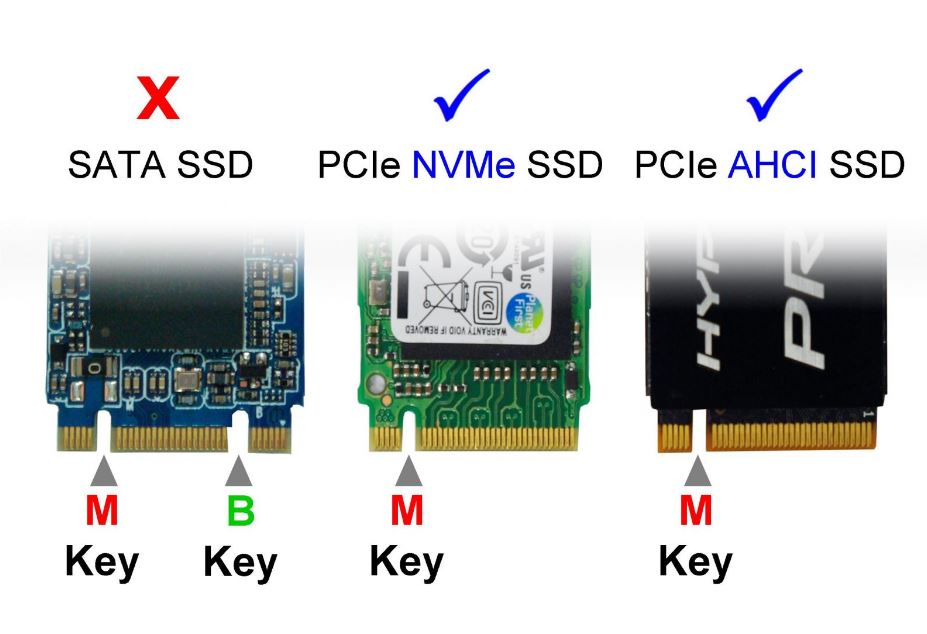
For the SATA drive to communicate with the system, it needs to have interconnect mode sets. The following are the most common interconnect modes.
- Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) – This is a system memory structure for computer hardware that exchanges the data between attached storage devices and host system memory. It gives developers and designers methods of detecting, configuring and programming SATA/AHCI adapters.
- Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) – Means through which the PC uses multiple disks as one. This is to increase performance or safeguard against disk failures.
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE) – It is a compatibility mode for storage devices and the system. The device run as an IDE or PATA drive.
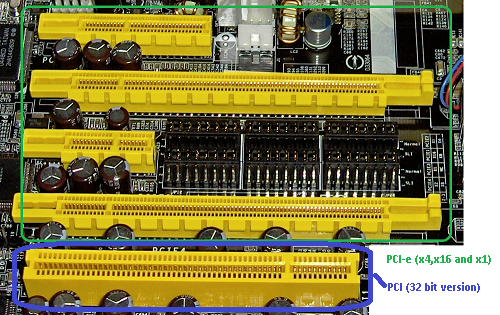
PCI Express
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe). It is used as an interconnect in motherboard expansion. This is the slot where graphics card, network card, sound card, RAID card are plug into. It was designed to replace PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards and to allow for more flexibility for expansion.
PCI Express has improved higher maximum bandwidth, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance-scaling, more detailed error detection and reporting, and hot-plugging.
Comparison between SATA and PCI Express
Serial AT Attachment (SATA) and Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) are widely used by SSDs that are available in the market. The differences between the two interfaces are discussed below:
1. The Connection
The SATA cables used to connect mechanical hard drives are the ones used for the SATA based SSDs. SATA III (most recent iteration) of the interface has a maximum throughput of 6 Gbps roughly 600 MB/s in real-time performance. Due to their popularity, the SSDs based on SATA III interface is the lowest priced SSDs available and are usually 2.5 inches.
The PCI Express interface has a high-speed serial expansion card format which uses point to point interface. This is the interface mainly used to connect Graphic cards. PCI Express based SSDs are plugged into an expansion slot on the motherboard that provides both data and power connection.
Unlike SATA based SSDs, PCI Express can allow more bandwidth trough faster signaling and multiple lanes. SSDs based on PCI Express has a direct connection to peripherals making them perform much better than SATA which uses cables to connect to the motherboard resulting in high latency.
2. Performance
The gap between SATA and PCI Express regarding performance is quite huge. As SATA III maxes out at 600 MB/s, two lanes of PCI Express 3.0 can provide up to 2000MB/s, more than three times the performance of SATA III-based SSD. The PCI Express consumes just 4% more power than a SATA III SSD.
3. SATA III SSDs
SATA III SSDs are commonly available in a 2.5-inch form factor utilizing SATA cables to connect to the motherboard. In case there is an indirect connection using cables, this will result in high latency which affects the maximum potential of the SSD.
4. PCI Express SSDs
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) allows SSD to make effective use of high-speed PCIe bus in a computer. PCIe is the same interface that’s used by graphics cards, sound cards, and Thunderbolt. For example, PCIe 3.0 offers up to 1 GB/s per lane. If the card is put in a four-lane slot, you’ll get four times the bandwidth which is up to 4 GB/s. NMVe being so fast is being considered as a replacement for the AHCI protocol used by most SATA based SSD today.
Also, PCIe based M.2 SSDs makes use of the NVMe protocol blistering fast speeds managing speeds of nearly 2000 MB/s. Intel Optane Memory based on PCI Express is claimed to be 4.42 times faster than a NAND based NVMe SSD regarding I/O operations per second.
5. Pricing
Although the prices of SATA III-based SSDs have come down by a considerable margin, the fastest SATA based SSD you can buy, Samsung 850 Pro costs approximately $1000 for the 2TB variant while the newer and NVMe SSDs cost hundreds of dollars depending on the storage space needed.
Which SSD interface is better?
From the comparison above then, we can conclude that the PCI Express is better than the SATA SSD interface.
Although the PCI Express has a relatively higher cost and a higher power input of around 4%, it is better compared to SATA SSD interface. This is because;
- PCI Express interface provides both data and power connection which allows for a higher bandwidth through faster signaling and multiple lanes.
- SSDs based on PCI Express has a direct connection to peripherals making them perform much better than SATA which uses cables to connect to the motherboard resulting in high latency.
- PCIe have higher speeds than the SATA SSD. They have speeds that will reach speeds of up to 2000MB/s compared to the 500 MB/s by SATA SSDs.
Therefore the PCI Express is technologically better than SATA SSDs since less time is used.